Stability of co-annular active and passive confined fluids
The translation and shape deformations of a passive viscous Newtonian droplet immersed in an active nematic liquid crystal under circular…
Physical Review Fluids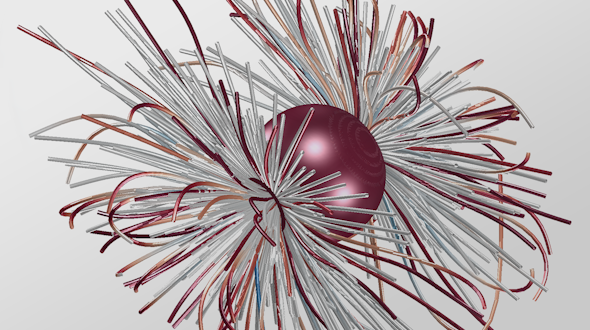
Examples are the organization and dynamics of the nucleus, the structure and assembly of spindles, the positioning and transport of cellular organelles, and fluid-structure problems in biology. To address these, often in close collaboration with experimental collaborators, we build numerical and theoretical models from the ground up, revealing how the known mechanics of individual components give rise to collective behavior. Many such phenomena occur only within dense, highly interacting systems, inaccessible to standard techniques. To probe such regimes requires the development of fast and scalable algorithms for many-component systems, and of coarse-grained models that can be analyzed and simulated.
Biophysical Modeling Lab
We begin by gathering high-quality data through experiments, performed either in-house or by our collaborators. This step is critical for identifying patterns, proposing hypotheses, and pinpointing the key constituents driving the biological phenomenon.
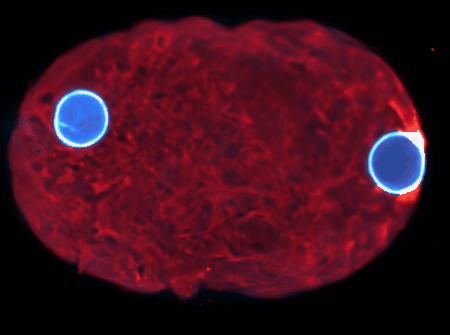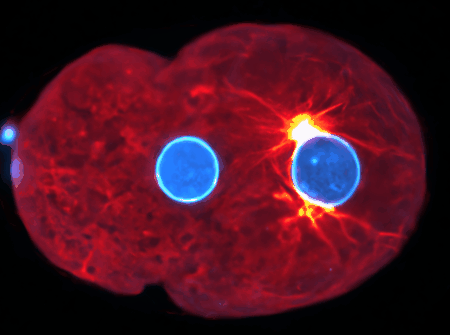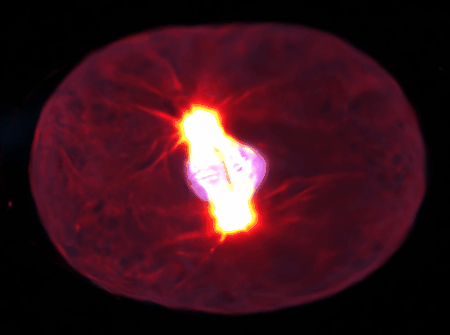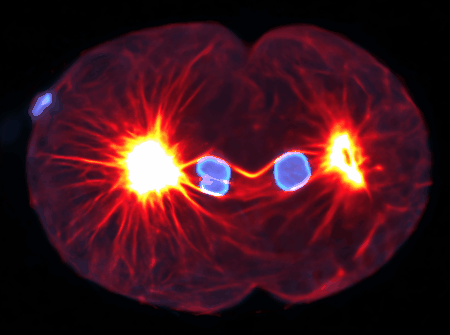
Using state-of-the-art computational tools and high-performance computing resources, we translate our observations into detailed simulations. These allow us to explore complex, multi-scale phenomena with biologically-relevant particle numbers.
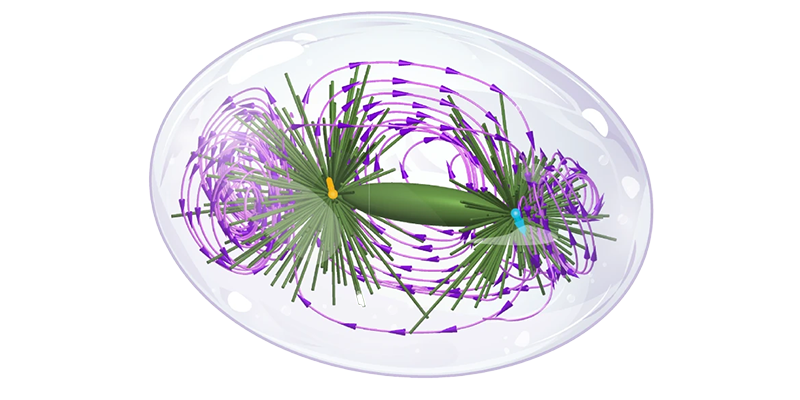
Insights from microscopic simulations are distilled into coarse-grained models that encapsulate the core mechanisms of the systems under investigation. These models strike a balance between complexity and interpretability, enabling robust predictions and theoretical advancements.
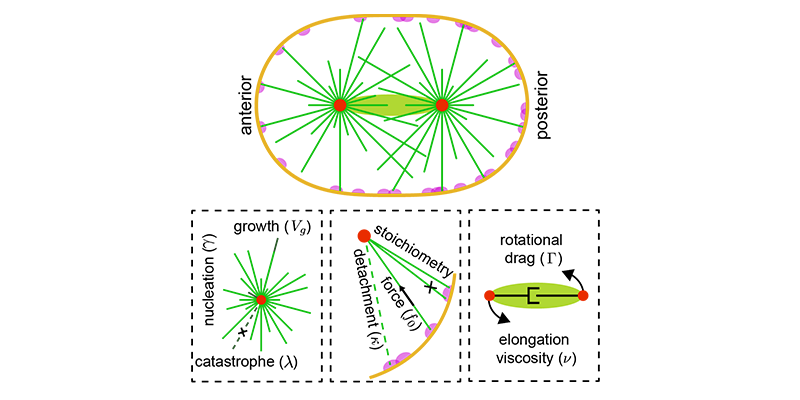
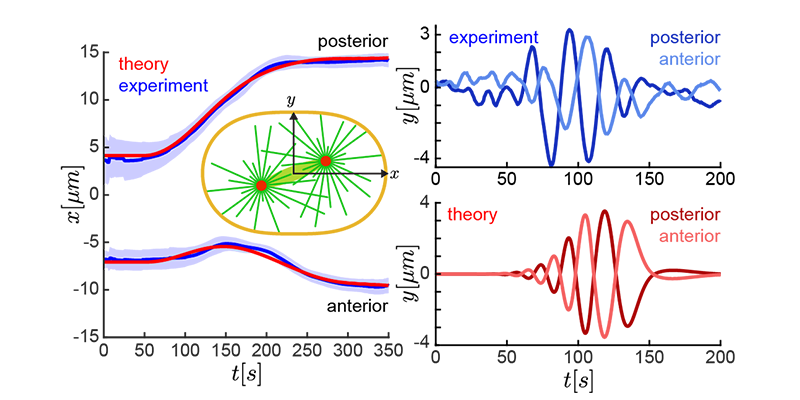
We rigorously analyze both simulations and models to uncover new insights, identify critical parameters, and validate results against experiments. The latter often involves advanced statistical methods, machine learning techniques, and collaboration with domain experts.
The translation and shape deformations of a passive viscous Newtonian droplet immersed in an active nematic liquid crystal under circular…
Physical Review FluidsAn obstacle is immersed in an externally driven 2D Stokes or Navier-Stokes fluid. We study the self-equilibration conditions for that…
arXiv:2508.05481How thousands of microtubules and molecular motors self-organize into spindles remains poorly understood. By combining static, nanometer-resolution, large-scale electron tomography…
arXiv:2507.22273
This is the simulation tool for tracking assemblies of microtubules driven by motor proteins.

SkellySim is a simulation package for simulating cellular components such as flexible filaments, motor proteins, and arbitrary rigid bodies.

This is a numerical computation package for various single- and double-layer kernels for Laplace and Stokes operators in boundary integral methods, implemented on top of the highly-optimized kernel independent fast-multipole method package PVFMM.